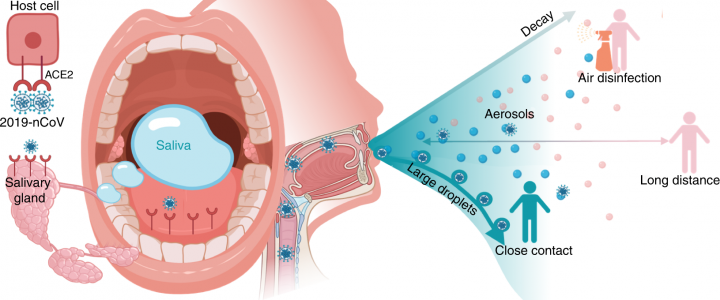
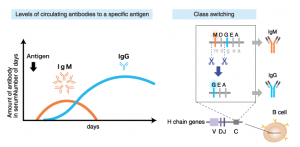
It is a clear fluid produced by various glands in the mouth area. Saliva is an important part of a healthy body. It is composed mainly of water. But saliva also contains important substances your body needs to digest food and keep your teeth strong.
Saliva is important because:
- Keeps your mouth moist and comfortable.
- It helps you chew, taste and swallow.
- It fights germs in the mouth and prevents bad breath.
- It has proteins and minerals that protect tooth enamel and prevent cavities and gum disease.
- Helps keep dentures securely in place.
You make saliva when you chew. The harder you chew, the more saliva you will produce. Sucking on hard candy or a cough drop also helps produce saliva. The glands that produce saliva are called salivary glands. Salivary glands are located inside each cheek, at the bottom of the mouth, and near the front teeth next to the jawbone.
There are six major salivary glands and hundreds of minor ones. Saliva moves through tubes called salivary ducts. Normally, the body produces 2 to 4 pints of saliva a day. Usually, the body produces the most saliva in the late afternoon. He does the least amount at night. But everyone is different. What doctors consider a normal amount of saliva varies quite a bit. That makes diagnosing saliva problems challenging.
Very little saliva
Certain illnesses and medications can affect the amount of saliva you produce. If you don’t produce enough saliva, your mouth can become quite dry. This condition is called dry mouth (xerostomia). A dry mouth causes the gums, tongue, and other tissues in the mouth to swell and feel uncomfortable. Germs thrive in this type of environment. A dry, germ-filled mouth leads to bad breath. A dry mouth also makes you more likely to quickly develop cavities and gum (periodontal) disease.
That’s because saliva helps remove food particles from your teeth. This helps reduce the risk of cavities. If you have a dry mouth, you may also notice that things don’t taste like they used to. Dry mouth is common in older adults, although the reasons are not clear. Diseases that affect the whole body (systemic disorders), poor nutrition and the use of certain medications are thought to play a key role. Lack of saliva and dry mouth can be caused by:
- Certain diseases such as HIV/AIDS, Sjogren’s syndrome, diabetes, and Parkinson’s
- Blockage in one or more tubes that drain saliva (salivary duct obstruction)
- Chemotherapy and radiotherapy
- Dehydration
- “fight or flight” stress response
- Structural problem with a salivary duct
- smoking cigars
Hundreds of commonly used medications are known to affect saliva flow and cause dry mouth, such as:
- antihistamines
- medication for anxiety
- appetite suppressants
- Certain types of blood pressure medications
- Diuretics (water pills)
- most antidepressants
- Certain analgesics (analgesics)
Always ask your health care provider about the side effects you may have from taking medicine.

What can I do if I have very little saliva?
Try these tips to help keep your salivary glands healthy and your mouth moist and comfortable:
- drink plenty of water
- Chew sugar-free gum
- Sugar free candy sucks
If dry mouth persists, your doctor or dentist may recommend that you rinse your mouth with artificial saliva. Artificial saliva is a liquid or spray that is sold without a prescription. It can be used as many times as necessary. Artificial saliva helps keep the mouth moist and comfortable. But it doesn’t contain the proteins, minerals, and other substances found in real saliva that help with digestion.
Too much saliva
Too much saliva is usually not something to worry about unless it persists. It is normal to produce more or less saliva depending on what you eat or drink. Your body usually takes care of the excess saliva by swallowing more. You may produce too much saliva if:
- One or more salivary glands are overactive
- you have trouble swallowing
It is normal for your salivary glands to go into overdrive when you eat very spicy foods. The taste buds on your tongue play an important role in the amount of saliva you produce. Put something spicy or very sour in your mouth and your taste buds react by telling your body to produce more saliva. Acidic foods tend to cause much more saliva than sweet foods. If excess saliva bothers you, try changing your diet.
If you have a lot of salivae all the time, let your health care provider know. It could be the side effect of a medication or the result of a medical condition or disease. If you have trouble swallowing, you may feel like you have a lot of saliva in your mouth and you may drool. Chronic drooling is most often seen in people who have poor muscle control over their face and mouth.
Diseases and health conditions that can cause too much saliva to include:
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also called Lou Gehrig’s disease
- Bell’s palsy
- Cerebral palsy
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
- An enlarged tongue (macroglossia)
- intellectual disability
- Parkinson’s disease
- Poisoning
- Pregnancy (usually seen in those with extreme nausea and vomiting)
- Rage
- Career
Medications that can cause too much saliva to include:
- Some anti-seizure medications such as Klonopin (clonazepam)
- Schizophrenia medication called clozapine (Clozaril, Fazaclo ODT)
- Salagen (pilocarpine), which is used to treat dry mouth in people receiving radiation therapy
What can I do if I have too much saliva?
Treatment for excess saliva depends on the cause of the problem. May include:
- prescription medicine
- Botox injections
- Surgery
Your doctor will likely first recommend a prescription medication to help reduce the amount of saliva you make. Such drugs include glycopyrrolate and scopolamine. Common side effects include trouble urinating, fast heartbeat, dizziness, blurred vision, and drowsiness. If you have severe drooling, your doctor may suggest Botox injections into one or more salivary glands.
This treatment is considered safe, but the results only last a few months. You will need to have more Botox injections in the future. In severe cases, surgery may be done to remove a salivary gland or reroute a salivary duct. This type of surgery usually provides a permanent cure for excess saliva.