Nutrient adaptation is vital in limiting environments for the promotion of microbial progress and survival. In microbial techniques, iron is a vital part for many mobile processes, and bioavailability varies drastically amongst completely different situations.
In the bacterium, Klebsiella pneumoniae, the affect of iron limitation is thought to change transcriptional expression of iron-acquisition pathways and affect secretion of iron-binding siderophores, nonetheless, a complete view of iron limitation on the protein stage stays to be outlined.
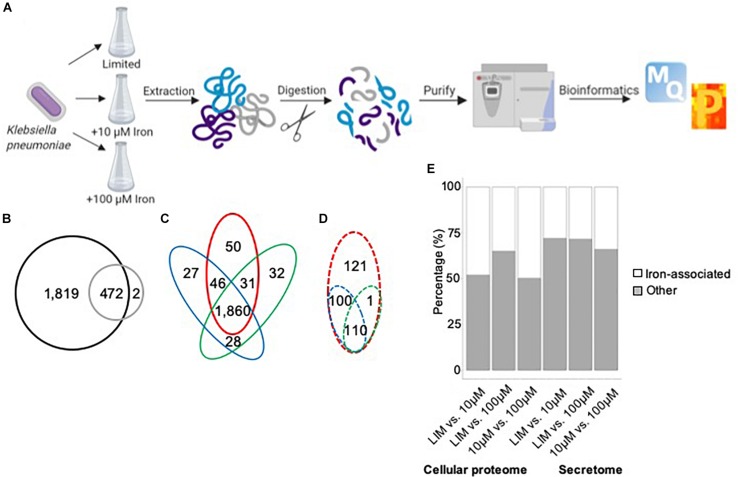
Here, we apply a mass-spectrometry-based quantitative proteomics technique to profile the worldwide affect of iron limitation on the mobile proteome and extracellular setting (secretome) of Ok. pneumoniae.
Our information outline the affect of iron on proteins concerned in transcriptional regulation and emphasize the modulation of an enormous array of proteins related to iron acquisition, transport, and binding. We additionally establish proteins in the extracellular setting related to typical and non-conventional modes of secretion, in addition to vesicle launch. In specific, we show a brand new function for Lon protease in selling iron homeostasis outdoors of the cell.
Characterization of a Lon protease mutant in Ok. pneumoniae validates roles in bacterial progress, cell division, and virulence, and uncovers novel degradation candidates of Lon protease related to improved iron utilization methods in the absence of the enzyme. Overall, we offer proof of distinctive connections between Lon and iron in a bacterial system and counsel a brand new function for Lon protease in the extracellular setting throughout nutrient limitation.
Proteomic evaluation of mixed IGF1 receptor focused remedy and chemotherapy identifies signatures related to survival in breast most cancers sufferers.
Clinical, epidemiological and experimental information recognized the insulin-like progress factor-1 receptor (IGF1R) as a candidate therapeutic goal in oncology.
While this paradigm is predicated on well-established organic information, together with the potent anti-apoptotic and cell survival capabilities of the receptor, most Phase III medical trials designed to focus on the IGF1R led to disappointing outcomes. The current research was geared toward evaluating the speculation that mixed remedy composed of selective IGF1R inhibitor together with classical chemotherapy is perhaps simpler than particular person monotherapies in breast most cancers remedy.
Analyses included complete measurements of the synergism achieved by varied mixture regimens utilizing the CompuSyn software program. In addition, proteomic analyses had been performed to establish the proteins concerned in the synergistic killing impact at a world stage.
Data introduced right here demonstrates that co-treatment of IGF1R inhibitor together with chemotherapeutic medication markedly improves the therapeutic effectivity in breast most cancers cells.
Of medical relevance, our analyses point out that prime IGF1R baseline expression could function a predictive biomarker for IGF1R focused remedy. In addition, we recognized a ten-genes signature with potential predictive worth. In conclusion, using a sequence of bioinformatics instruments make clear a number of the organic pathways that is perhaps accountable for synergysm in most cancers remedy.